The term Gum Disease has been circulating in television commercials lately. When you see those commercials, do you wonder if you are at risk for gum disease? All this new attention to gum disease and what it all means may have you asking questions. We are here to help answer questions and sort through the information.
What is Gum Disease?
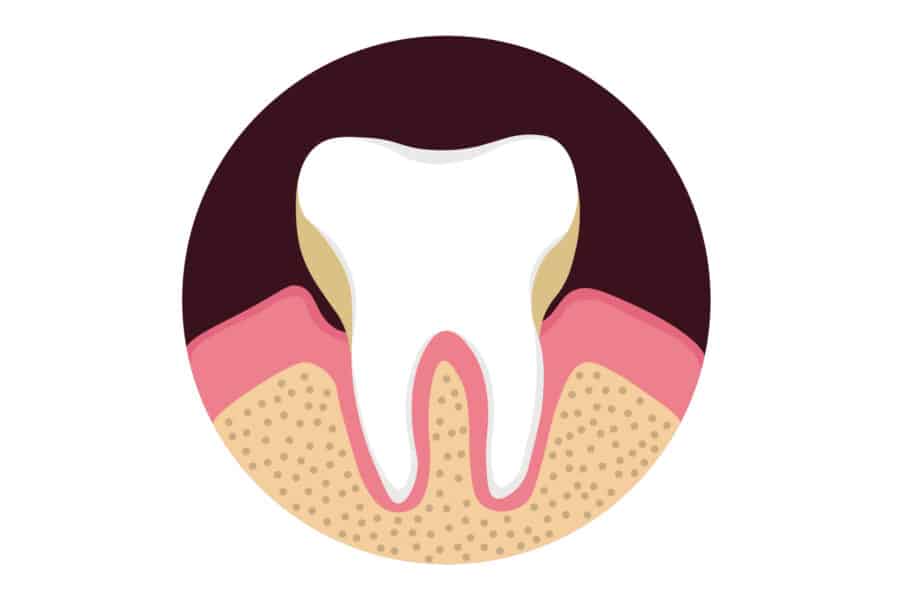
Gum disease, which is also called periodontal disease is an infection within your gum tissue, supporting ligaments, and jawbone. This infection is caused by harmful bacteria that is present in plaque, a soft and sticky substance on our teeth that forms daily. Without professional care, this disease can worsen and cause gum and bone loss that can lead not only to tooth loss but can also affect your overall health.
What are the Signs of Gum Disease?
Some common symptoms of gum disease include:
- Gums that bleed when brushing or flossing
- Gums that appear red, puffy, or are tender
- Bad breath or a persistent bad taste in your mouth
- Gums that appear receded or look pulled away from your teeth
- Teeth that feel loose or shifted
- Changes in the way your teeth fit together
- Changes in the way your partials or other dental work fits
While some people can have clear signs and symptoms of gum disease, others can have it with little or even no symptoms. The best way to know if you have any form of gum disease is to visit your dentist for a full-mouth evaluation to determine your gum health and if you have any type of disease.
What are the Types of Gum Disease?
Generally, there are two types of gum disease, Gingivitis and Periodontitis.
Gingivitis is the first and earliest stage of gum disease that is an inflammation of your gum tissue caused by harmful bacteria present under your gums. These bacteria produce toxins that irritate your gums and cause you body to react by sending inflammatory cells in response. This inflammation leads to redness, puffiness, and bleeding of your gums.
If noticed early, gingivitis can usually be easily treated with improved homecare and professional dental cleanings. With simple, additional attention to your mouth and gums, inflammation can be reduced, and gum condition improved because the gingivitis stage does not cause permanent damage to gum tissue, ligaments, and bone support.
However, studies have shown that once we have gingivitis, certain memory cells may remain that may make us more vulnerable to future infection. Therefore, good homecare and regular dental visits are important.
Periodontitis is second and more harmful type of gum infection. At this stage, the infection from the harmful bacteria causes damage to the tissues and bone that are supporting your teeth. This damage creates deeper space between your tooth and gum called a periodontal pocket. These pockets are impossible for you to clean at home and even difficult to clean during regular professional dental cleanings.
Without proper treatment, periodontitis can advance to a more severe gum infection that continues to destroy your gums and jawbone that support your teeth. Without support, your teeth can shift, loosen, and eventually need to be removed.
Periodontitis does not just affect your mouth. Studies show that active gum infections can affect your overall health. Links between periodontitis and several medical conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and stroke mean that identifying and treating your gum infection is important for your overall health.
At this stage, your dentist may refer you to a periodontist who is a specialist in the treatment of gum disease.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Although bacteria cause the periodontal infection, other health and lifestyle factors may exist that can worsen the disease progression. Those risk factors are categorized as either primary or secondary risk factors.
Primary risk factors may include genetics, health issues such as diabetes, tobacco use, and poor homecare. Secondary risk factors may include long intervals between dental cleanings, certain medications that can affect your mouth, hormonal changes, and stress.
Your teeth themselves may also be part of the problem if you have misaligned or missing teeth, grind or clench your teeth, or have obstacles to brushing like large fillings or braces.
Identifying risk factors is one of the first steps in establishing the best therapies to treat your disease.
How Can It Be Treated?
Patients who have gingivitis can generally be treated easily with a regular dental cleaning and proper home care instruction. Since harmful bacteria forms in your mouth every day, proper removal is essential. Your dentist or dental hygienist may offer home care tips and tools to help you remove the bacteria more effectively.

Since nobody can remove all the bacteria at home, you will be advised to visit your dental office regularly for professional cleanings and exams to monitor your oral health.
Patients who have periodontitis generally require additional gum treatment by the periodontist. Because the infection is more severe, the stage of periodontitis will determine treatment needs. Those treatments can be non-surgical and surgical depending on the level of your infection.
Non-surgical periodontal treatments are referred to as Phase 1 Therapy. They usually involve several visits with a dental hygienist in your periodontal office. During these visits, your hygienist will perform a procedure called Scaling & Root Planing to clean the pockets with special tools that will remove the toxins and debris that are actively causing your infection. This procedure is non-invasive and requires no downtime after treatment.
Surgical periodontal treatments are referred to as Phase 2 Therapy. They can involve traditional periodontal surgery or LANAP® dental laser therapy. While both therapies treat the active infection, they also help to repair the damage to your tissue and bone that has been caused by the infection.
Traditional periodontal surgery involves incisions to access the areas of disease so that the periodontist can repair them. After repair, your periodontist will place sutures, provide after-care instructions, and see you in a few weeks for removal of the stitches.
The LANAP® Protocol is a less invasive way to treat and repair damage to your oral tissues. With laser therapy, your periodontist can achieve the same and often better results as traditional therapy but without the cutting & stitches. This means that LANAP® offers effective treatment with less discomfort and faster recovery.
Your periodontist will determine which treatment is best for your level of infection.
What Are Risks from Gum Disease?
Because gum disease is an infection, it not only affects your mouth and can cause tooth pain and loss but can also negatively affect your overall health and well-being. Therefore, treating your gum disease can offer you ways to improve your overall health and happiness.
Your Health
Having an active infection in your mouth triggers an inflammatory response from your body to protect itself from bacteria that is damaging your cells. Whether you have gingivitis or periodontitis, your body is sensing an infection, which triggers a protective inflammatory response. These inflammatory responses to the infection can sometimes actually make your gum disease progress more quickly and become more severe.
The oral inflammation can also affect the rest of your body as well, which is called an oral-systemic relationship. This relationship basically means that your oral heath is connected to overall health because the inflammatory response moves through your whole body. Studies have shown that a relationship exists between gum disease and other systemic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, stroke, respiratory diseases, Alzheimer’s disease, osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, pre-term births, and certain types of cancer.
Because inflammation contributes to so many health issues, treating active gum infection is essential for living a healthier life.
Your Happiness
Not only does having gum disease affect your physical health, it can also affect your sense of well-being as well. Having a healthy smile boosts mood and self-confidence. When you have gum disease, you may not smile as often or feel self-conscious about speaking in public or even among friends or co-workers. Therefore, treating gum disease can improve your smile and boost your mood and self-confidence.
Your Dental Professionals are Here to Help!
The first step to a healthier mouth is to visit your dentist for a full evaluation. Our compassionate staff of dental professionals are here to help you achieve improved oral health, thus better overall health!